ARD (broadcaster)
 Logo since December 2019 | |
| Type | Broadcast radio, television and online |
|---|---|
| Country | Germany |
| Availability | National International |
| Owner | Independent[1] |
Key people | Florian Hager (HR), Chairman |
Launch date | 5 June 1950 |
Official website | www |

ARD[a] is a joint organisation of Germany's regional public-service broadcasters. It was founded in 1950 in West Germany to represent the common interests of the new, decentralised, post-war broadcasting services – in particular the introduction of a joint television network.
The ARD has a budget of €6.9 billion, 22,612 employees and is the largest public broadcaster network in the world.[2][3][4] The budget comes primarily from a mandatory licence fee which every household, company and public institution, regardless of television ownership, is required by law to pay. For an ordinary household the fee is €18.36 per month, as of 2023. Households living on welfare are exempt from the fee. The fees are not collected directly by the ARD, but by the Beitragsservice (formerly known as Gebühreneinzugszentrale GEZ), a common organisation by the ARD member broadcasters, the second public TV broadcaster ZDF, and Deutschlandradio.
ARD maintains and operates a national television network, called Das Erste ("The First [Channel]") to differentiate it from ZDF, a.k.a. "das Zweite" ("The Second [Channel]"), which started in 1963, as a separate public TV broadcaster. The ARD network began broadcasting on 31 October 1954 under the name of Deutsches Fernsehen ("German Television"), becoming Erstes Deutsches Fernsehen ("First German Television") with a corporate redesign in 1984; it adopted its current short name (Das Erste) in 1994. ARD's programmes are aired over its own terrestrial broadcast network, as well as via cable, satellite and IPTV.
ARD also produces two free-to-air channels (one and Tagesschau24) and participates in the production of Phoenix (current events, news and documentaries), KiKa (kids-oriented), 3sat (cultural-oriented), arte (Franco-German cultural programming), and Funk (teenage-oriented, online only).
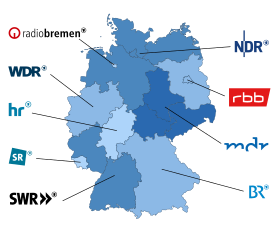
ARD's programming is produced by its regional members (see also Institutions and member organizations) (Bayerischer Rundfunk (BR), Hessischer Rundfunk (HR), Mitteldeutscher Rundfunk (MDR), Norddeutscher Rundfunk (NDR), Radio Bremen, Rundfunk Berlin–Brandenburg (RBB), Saarländischer Rundfunk (SR), Südwestrundfunk (SWR) and Westdeutscher Rundfunk (WDR)), which operate 54 regional and local radio stations and seven regional TV networks, some of which have opt-outs at during the day.[clarification needed] Deutsche Welle, Germany's international broadcaster, is also a member of ARD.
History
[edit]Name
[edit]- German: "Arbeitsgemeinschaft – der öffentlich-rechtlichen Rundfunkanstalten – der Bundesrepublik Deutschland"
- 'Consortium' ("Working group") – of the public-law broadcasting institutions‡ – of the Federal Republic of Germany'
‡public-law broadcasting institutions means broadcasters which are not privately owned (German: Privatradio and Privatfernsehen) and are not governmental radio or TV. ARD is not 'owned by' anybody, particularly not by "Germany" (meaning its government/federal state). ARD members like BR (Bayerischer Rundfunk) are not owned by their Land (state and its government, here Bavaria), either. With the Rundfunkfreiheit (freedom of broadcasting), they have an independent position (within a legal framework).
1940s and 1950s
[edit]The winning Allies of World War II determined that German radio after World War II would not broadcast the same propaganda as the pre-war Reichs-Rundfunk-Gesellschaft ("Reich Broadcasting Company"). A federal structure, the renunciation of state influence and the avoidance of economic dependence were to be the key of the radio and TV institutions under public law (öffentlich-rechtliche Rundfunk- und Fernsehanstalten, public radio and television organisations). The legal form of the new entity was Anstalt des öffentlichen Rechts ("Institution under Public Law"), a non-government and nonprofit organisation with its own administration under the control of two commissions, the Rundfunkrat (Broadcasting Council, responsible for the programmed content) and the Verwaltungsrat (Administration Council, responsible for management and infrastructure), in which different stakeholders from German public life were represented.
ARD's founding members were Nordwestdeutscher Rundfunk (NWDR), the station for the former British zone, Südwestfunk (SWF), the station in the French zone, and four stations located in the former American sector— Bayerischer Rundfunk (BR), Süddeutscher Rundfunk (SDR), Hessischer Rundfunk (HR), and Radio Bremen (RB). The new entity was financed by an obligatory fee that every German household with at least one radio receiver paid. Each station received the money collected in its state. Larger ARD members subsidised smaller ones up to a certain extent.
In 1947, American military governor Lucius D. Clay declared diversity of public opinion as the main aim of post-war media policy. Individuals aligned with the post-war Allied forces in their respective sectors of Germany had a local influence on local regional broadcasters. NDR cites the influence of Hugh Greene on the early years of their organisation.

After the creation of individual broadcasting agencies for most German federal states these principles were further consolidated by Länder broadcasting laws, decisions of the Federal Constitutional Court (Bundesverfassungsgericht), and state treaties between the Länder. ARD members are thus (at least nominally) free of government influence and rely for only a small part of their income on advertising (1995: ten percent). They are financed mainly from licence fees from radio and TV owners, which are set through a complex political process. The mandated aim of the ARD corporations is not only to inform and to entertain but also to encourage the integration of various parts of society and allow minorities a say in programming.
In the 1950s the ARD radio services became the major factor of the mass media system in West Germany. As early as 1952 the ARD radio stations had ten million listeners. However, the radio stations operated on a regional level, and it was only the development of a television umbrella that helped the ARD to establish itself nationwide. The broadcasting of a countrywide TV broadcast service was the goal of the ARD from the outset and the go-ahead for this was given at the end of 1952. The same year ARD was admitted as a fully active member of the European Broadcasting Union and the "German sound archive", now German Broadcasting Archive (DRA, Deutsches Rundfunkarchiv), was established as a joint facility of the ARD.
In 1955 the founding member NWDR ("Nordwestdeutscher Rundfunk", English: "North-West German Broadcasting") split into today's NDR and WDR. The year before (1954) the smaller SFB was split off. The first daily news feature, the Tagesschau, went on the air from Hamburg in 1952. The famous 8:00 pm chime and announcement "Hier ist das Erste Deutsche Fernsehen mit der Tagesschau" ("This is the first German television channel with the Tagesschau") remains an ARD hallmark today. The broadcast attracts an average of 8 million viewers.
1960s–1980s
[edit]After starting with a mere two-hour schedule per night, television became more widespread in Germany in the 1960s. Color broadcasts were introduced in 1967. Without competition from private broadcasters (other than the francophone Europe 1 and the multilingual RTL (Radio-Television Luxembourg) radio programs), the ARD stations made considerable progress in becoming modern and respected broadcasters. ZDF (Zweites Deutsches Fernsehen, Second German Television), a second public television broadcaster with a centralized national organization structure, began its programming in 1963, but ARD would encounter no private competition in Germany until 1984. The ARD stations have also been a significant force in German politics; such investigative news magazines as Monitor and Panorama still reach millions of viewers every week. The environmental movement increased in popularity during the 1980s largely as a result of the disclosures made by ARD.
When private/commercial German-language broadcasters were admitted in Germany by federal law in the mid-1980s, ARD television made subtle changes, adapting somewhat by producing programs oriented to a larger audience for their national networks and shifting many cultural and news programs to the regional networks and to newly created niche channels.
Informational television programs and the orientation of "Deutschlandfunk" (Germany's national public radio station, associated with, but not a member of the ARD) programs towards the GDR were of importance to the eventual collapse of the GDR.[citation needed] Established in 1974, the ARD bureau in East Berlin made ARD television the most important source of information for GDR citizens,[citation needed] eighty percent of whom could watch what they referred to as "Westfernsehen". Notwithstanding obstruction on the part of GDR authorities and the repeated expulsion of their correspondents, the ARD-Tagesschau and Deutschlandfunk transmitted a report about the Leipzig Monday Demonstrations (which started on 4 September 1989) as early as September 1989.
1990s
[edit]After the unification and the closure of the Deutscher Fernsehfunk, two new regional broadcasters were established in the East, becoming ARD members in 1992. These were originally the Mitteldeutscher Rundfunk (MDR, English: "Central German Broadcasting"), and Ostdeutscher Rundfunk Brandenburg (ORB, English: "East German Broadcasting Brandenburg"). The existing NDR service expanded into the north-east, where it also covered Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. The ORB service has since merged with the former Sender Freies Berlin (SFB, English "Radio Free Berlin") to become Rundfunk Berlin-Brandenburg (RBB, English: "Berlin-Brandenburg Broadcasting") in 2003.
Another merger took place between two member organisations of the ARD in 1998. The former Süddeutscher Rundfunk (SDR, English: "Southern German Broadcasting") and Südwestfunk (SWF, English: "Southwestcast") became Südwestrundfunk (SWR, English: "Southwest Broadcasting") on 1 October 1998.
Programming
[edit]Radio
[edit]Today, ARD member stations usually produce their radio programming. Some ARD member stations usually collaborate for common radio services (an example is Nordwestradio, a culture-oriented radio station co-produced by Radio Bremen and NDR). Most ARD stations, however, will have at least a news-oriented radio station, a classical music station, a youth-oriented station, and a cultural station. At night some stations will relay common night programming produced on a rota system by the ARD stations themselves. There are four common night programming services: Hitnacht (light music), Nachtkonzert (classical music), Infonacht (all news), and Popnacht (pop music). Most services are on the FM broadcast band, though some services are also available on DAB.
A similar network intended for national coverage is called Deutschlandradio, however, Deutschlandradio is not an ARD member – instead, Deutschlandradio is controlled by both ARD and ZDF. Deutschlandradio provides two terrestrial radio services: Deutschlandfunk (DLF), a news-oriented service, and Deutschlandfunk Kultur, a culture-oriented service. It also provides a science-orientated internet channel: Deutschlandfunk Nova.
ARD's best-known radio station outside Germany is Deutsche Welle, which broadcasts its radio services around the world in many languages, mostly on analogue shortwave radio, online, and FM partner stations. Deutsche Welle has no FM distribution in Germany.
"Archivradio"[5] is an ARD internet radio station that streams raw audio from German sound archives, mainly the ARD radio archives and the DRA. The program is accompanied by a web portal run by the ARD-member SWR, with background information on the original sounds aired.
Television
[edit]The main television channels of the ARD are the nationwide Das Erste and seven regional channels operated by the different regional broadcasting institutions. These channels were available on the analogue terrestrial transmitters until the shutdown of the analogue transmitters started in 2003. Das Erste and the third programmes, like the radio stations, are principally funded by licence fees, with a very limited amount of on-air advertising.
Das Erste broadcasts nationwide 24 hours a day. However, the schedule does include four and a half hours of joint programming with ZDF each weekday, in the form of the news programmes Morgenmagazin (on air 5.30–9.00) and Mittagsmagazin (13.00–14.00), which the two organizations take weekly turns to produce. Audience share (March 2008):12.5%, from 14 to 49 years 6.9%.
The regional members of ARD all, jointly (NDR/rb and SWR/SR) or separately, operate their own regional channels, known collectively as die Dritten ("the Third Programmes") – before recent rebranding, most of these stations had names like West 3 and Hessen 3. The schedules of these regional channels also include sub-regional opt-outs at certain times, in particular for local news.
- BR Fernsehen from Bayerischer Rundfunk (sub-regional opt-outs: Altbayern und Schwaben (South), Franken (North))
- hr-fernsehen from Hessischer Rundfunk
- MDR Fernsehen from Mitteldeutscher Rundfunk (opt-outs: state programmes for Saxony, Sachsen-Anhalt, Thuringia)
- NDR Fernsehen from Norddeutscher Rundfunk (opt-outs: state programmes for Lower Saxony, Schleswig-Holstein, Hamburg, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and rb.tv from Radio Bremen)
- RBB Fernsehen from Rundfunk Berlin-Brandenburg (opt-outs: separate state programmes)
- SWR Fernsehen from Südwestrundfunk – in collaboration with SR Fernsehen (opt-outs: state programmes for Baden-Württemberg, Rhineland-Palatinate and SR Fernsehen from Saarländischer Rundfunk)
- WDR Fernsehen from Westdeutscher Rundfunk. (11 local opt-outs within North Rhine-Westphalia)
ARD has three additional channels as part of their ARD Digital package:
- Tagesschau24 – television news channel
- One – entertainment television channel
- ARD-alpha – educational programming
ARD is also involved in several joint venture channels:
- 3sat with ZDF, ORF and SRG: a cultural channel
- KI.KA with ZDF: a children's channel
- Arte with ZDF and France Télévisions: a Franco-German cultural channel
- Phoenix with ZDF: a news and documentary channel, focussed on showing press conferences and political debates in the German parliament live, in addition to historical and political features.
The international broadcaster Deutsche Welle also produces television services; however, these services are mostly available via satellite.
Podcasts
[edit]The Tagesschau, produced by the ARD on a nightly basis, is available on the ARD website as a podcast (available as audio-only or as audio and video). Other audio programs from the ARD's members (e.g., BR, MDR) and Deutsche Welle are available as podcasts, through their respective websites.
Institutions and member organizations
[edit]| Regional broadcaster (translation) | Abbreviation | Main office location(s) | Income 2004 (Millions of Euro) | Year of establishment | Region of coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bayerischer Rundfunk (Bavarian Broadcasting) | BR | Munich | 806 | 1949 | Bavaria |
| Deutsche Welle ("German Wave") | DW | Bonn | Financed through taxes | 1953 | International |
| Hessischer Rundfunk (Hessian Broadcasting) | HR | Frankfurt | 383 | 1948 | Hesse |
| Mitteldeutscher Rundfunk (Central German Broadcasting) | MDR | Leipzig | 561 | 1991 | Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia |
| Norddeutscher Rundfunk (North German Broadcasting) | NDR | Hamburg | 892 | 1956 | Hamburg, Lower Saxony and Schleswig-Holstein since 1955; Mecklenburg-Vorpommern since 1991. |
| Radio Bremen | RB | Bremen | 41 | 1945 | Bremen |
| Rundfunk Berlin-Brandenburg (Berlin-Brandenburg Broadcasting) | RBB | Berlin, Potsdam | 340 | 2003 | Berlin, Brandenburg |
| Saarländischer Rundfunk (Saarland Broadcasting) | SR | Saarbrücken | 64 | 1957 | Saarland |
| Südwestrundfunk (Southwest Broadcasting) | SWR | Stuttgart, Mainz, Baden-Baden | 922 | 1998 | Baden-Württemberg, Rhineland-Palatinate |
| Westdeutscher Rundfunk (West German Broadcasting) | WDR | Cologne | 1,067 | 1956 | North Rhine-Westphalia |

ARD has 30[6] correspondents' offices[7] in 26[8] countries.[9][10]
ARD operates several other companies and institutions, sometimes jointly with ZDF: Degeto Film, a television rights trader and production company; the German Broadcasting Archive (DRA – Deutsches Rundfunkarchiv); the Institute for Broadcasting Technology (IRT – Institut für Rundfunktechnik), responsible for research and development; the Fee Collection Service (Beitragsservice), and others.
ARD is a supporter of the Hybrid Broadcast Broadband TV (HbbTV) initiative that is promoting and establishing an open European standard for hybrid set-top boxes for the reception of broadcast TV and broadband multimedia applications with a single user interface.
Chairs of the ARD
[edit]| Term Begin |
Term End |
Name | Broadcaster |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 August 1950 | 2 February 1951 | Rudolf von Scholtz | BR |
| 3 February 1951 | 2 August 1951 | Eberhard Beckmann | HR |
| 3 August 1951 | 3 February 1952 | Adolf Grimme | NWDR |
| 4 February 1952 | 30 September 1952 | Walter Geerdes | RB |
| 1 October 1952 | 31 March 1953 | Fritz Eberhard | SDR |
| 1 April 1953 | 30 September 1953 | Friedrich Bischoff | SWF |
| 1 October 1953 | 30 September 1954 | Rudolf von Scholtz | BR |
| 1 October 1954 | 31 December 1955 | Eberhard Beckmann | HR |
| 1 January 1956 | 31 December 1956 | Fritz Eberhard | SDR |
| 1 January 1957 | 31 December 1957 | Walter Hilpert | NDR |
| 1 January 1958 | 31 December 1958 | Franz Stadelmayer | BR |
| 1 January 1959 | 31 December 1960 | Friedrich Bischoff | SWF |
| 1 January 1961 | 31 December 1962 | Hans Bausch | SDR |
| 1 January 1963 | 31 December 1964 | Klaus von Bismarck | WDR |
| 1 January 1965 | 31 December 1966 | Werner Hess | HR |
| 1 January 1967 | 31 December 1969 | Christian Wallenreiter | BR |
| 1 January 1970 | 31 December 1971 | Gerhard Schröder | NDR |
| 1 January 1972 | 31 December 1973 | Helmut Hammerschmidt | SWF |
| 1 January 1974 | 31 December 1975 | Hans Bausch | SDR |
| 1 January 1976 | 31 December 1977 | Werner Hess | HR |
| 1 January 1978 | 31 December 1979 | Friedrich-Wilhelm von Sell | WDR |
| 1 January 1980 | 31 December 1983 | Reinhold Vöth | BR |
| 1 January 1984 | 31 December 1985 | Friedrich Wilhelm Räuker | NDR |
| 1 January 1986 | 31 December 1987 | Willibald Hilf | SWF |
| 1 January 1988 | 31 December 1988 | Hans Bausch | SDR |
| 1 January 1989 | 31 December 1990 | Hartwig Kelm | HR |
| 1 January 1991 | 31 December 1992 | Friedrich Nowottny | WDR |
| 1 January 1993 | 31 December 1994 | Jobst Plog | NDR |
| 1 January 1995 | 31 December 1996 | Albert Scharf | BR |
| 1 January 1997 | 31 December 1998 | Udo Reiter | MDR |
| 1 January 1999 | 31 December 2000 | Peter Voß | SWR |
| 1 January 2001 | 31 December 2002 | Fritz Pleitgen | WDR |
| 1 January 2003 | 31 December 2004 | Jobst Plog | NDR |
| 1 January 2005 | 31 December 2006 | Thomas Gruber | BR |
| 1 January 2007 | 31 December 2008 | Fritz Raff | SR |
| 1 January 2009 | 31 December 2010 | Peter Boudgoust | SWR |
| 1 January 2011 | 31 December 2012 | Monika Piel | WDR |
| 1 January 2013 | 31 December 2015 | Lutz Marmor | NDR |
| 1 January 2016 | 31 December 2017 | Karola Wille | MDR |
| 1 January 2018 | 31 December 2019 | Ulrich Wilhelm | BR |
| 1 January 2020 | 31 December 2021 | Tom Buhrow | WDR |
| 1 January 2022 | 4 August 2022 | Patricia Schlesinger | rbb |
| 4 August 2022 | 31 December 2022 | Tom Buhrow | WDR |
| 1 January 2023 | 31 December 2024 | Kai Gniffke | SWR |
| 1 January 2025 | Florian Hager | HR |
Correspondents
[edit]Europe
[edit]| Studio | Broadcaster | Area of responsibility |
|---|---|---|
| Brussels | WDR | The largest ARD foreign studio and the only one with its own TV show (Europamagazin (WDR/SWR)). Responsible for Benelux and the EU as well as NATO. The office was established in 1961. After almost two years of construction, a new studio was opened in the new media house in EU City in 2008. DW employees and the head of the ARD liaison office also work there. The radio studio is divided into three groups with the respective leaders WDR, HR and SWR. There is also a radio studio from Deutschlandradio. |
| The Hague | WDR | Radio studio for the Netherlands |
| Geneva | SWR | TV and radio studio. Responsible for Switzerland, Liechtenstein, UN organizations, WHO, FIFA, IOC, etc. The studio has existed since the mid-1950s. |
| Istanbul | BR / SWR | Turkey, Northern Cyprus, (→ Studio Tel Aviv), including a liaison office in Tehran, Iran. |
| Kyiv[11] | WDR | Television and radio studio. Responsible for Ukraine and, if necessary, other areas in Eastern Europe. Established in 2023 as a result of the Russian invasion of Ukraine. |
| London | NDR | Television and radio studio. Responsible for the UK and Ireland. |
| Madrid | SWR / HR | Television and radio studio. Responsible for Spain, Portugal, Andorra, Gibraltar and since March 2004 also responsible for the Maghreb.[12] |
| Moscow | WDR | Television and radio studio. Responsible for Russia and all CIS states, as well as Mongolia and Georgia, and also for Ukraine until 2023 (opening of a new ARD studio in Kyiv). Closed briefly in 2022 in the wake of the Ukraine war and a new media law in Russia. |
| Paris | WDR | Television and radio studio. Responsible for France and Monaco. |
| Prague | MDR | Television and radio studio, responsible for Czech Republic and Slovakia. |
| Rome | BR | Tri-media studio: television, online and radio studio. Responsible for Italy, Malta, Greece, Vatican City. |
| Stockholm | NDR | Television and radio studio. Responsible for Scandinavia, Finland and the Baltics. The studio was moved from Riga to Stockholm in 1997. |
| Warsaw | WDR / RBB | TV and radio studio. Reporting about Poland. |
| Vienna | BR | Austria, two sub-offices in Belgrade and Sarajevo, responsible for Southeast-Europe. |
The radio studio in Strasbourg, which was closed in July 2010 and previously operated by SWR, was responsible for the European Parliament. Since then, reporting has been carried out from Brussels and Paris.
The ARD radio studio in Zurich was closed in August 2021. Since then, reporting has been carried out from Geneva.
Americas
[edit]| Studio | Broadcaster | Area of responsibility |
|---|---|---|
| Los Angeles | HR | United States, radio studio in West Coast, reporting primarily on California and Hollywood. Another office exists in San Francisco. |
| Mexico City | SWR/RBB | The studio in Mexico has existed since 1982 and is responsible for Central America, the Caribbean and northern South America (except Colombia). |
| New York City | WDR | UN/New York/Canada[13] The studio started as a one-man office in 1973, and in 1980 WDR expanded the office into a television studio. |
| Rio de Janeiro | SWR | The main studio for South America has been in Rio de Janeiro since April 2005, before that it was in Buenos Aires. The radio and television studios have been in Rio de Janeiro since 2022. |
| Washington, D.C. | BR/HR/MDR/NDR/SWR/WDR | USA overall/focus on politics Washington |
The ARD radio studio in Buenos Aires was closed in 2022. Since then, reporting has been carried out from Rio de Janeiro.
Africa and Middle East
[edit]| Studio | Broadcaster | Area of responsibility |
|---|---|---|
| Johannesburg | SWR | In addition to South Africa, the reporting area also includes Namibia, Zimbabwe, Lesotho, Eswatini, Mozambique, Angola, Botswana, Zambia and Malawi. The radio also covers Madagascar, La Réunion, Mayotte, Mauritius and the Comoros.[14] The ARD studio is based in a media complex and has had a radio correspondent since 1976 and a TV correspondent since 1977. Apart from the correspondents and assistants, all employees are South African. |
| Cairo | WDR / SWR | Main studio for the Arab World, North Africa to Sudan. In 2010, the ARD radio studios in Cairo (SWR) and Amman (WDR) became a joint studio based in Cairo under the joint management of SWR and WDR. The studio has locations in Amman and temporarily in Beirut or Dubai. |
| Nairobi | WDR | Nairobi is ARD's largest studio on the African continent and has existed since 1973.[15] |
| Rabat | HR | Pure radio office, responsible for 22 countries in West and North Africa. Reporting area: Algeria, Benin, Burkina Faso, Ivory Coast, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Cameroon, Cape Verde Islands, Liberia, Mali, Morocco, Mauritania, Niger, Nigeria, Sao Tomé and Principe, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Chad, Togo, Tunisia. |
| Tel Aviv | BR | Israel, Palestine |
The studio for Turkey and Iran (radio) is in Istanbul, see above. The ARD radio studio in Amman was closed in 2013. It only has a branch office in Cairo, from where reporting has been carried out ever since.
Logo
[edit]-
ARD's first logo used from the 1950s until 1970
-
ARD's second logo used from 1970 until 1984
-
ARD's third logo used from 1984 until 2003
-
ARD's fourth logo used from 2003 until 2019
-
ARD's fifth and current logo used since December 2019
Criticism
[edit]Criticism by political parties
[edit]Since it was founded in 2013, the German party AfD has accused the German broadcasters of being state-driven propaganda machines. This claim is heavily disputed. For example, a 2019 study from Oxford (p. 24) stated that the majority of the audience of German public broadcasters ARD, ZDF and "Deutschland Radio" are left-winged or left of the center of the political spectrum. The AfD took this to show that the broadcaster is biased and contributing to a left-shift in the political environment. The majority of German newspapers have responded that the AfD have misunderstood the Oxford study, and accused the AfD of spreading fake news. Another point of evidence offered is that ARD board member and Director for Programming Christine Strobl is not only a member of the CDU party herself, but also the daughter of Wolfgang Schäuble, a prominent CDU member of parliament. As Director for Programming she is in a position to stop or initiate the production of programs, but also potentially editorial decisions.[citation needed]
Neutrality
[edit]After the ARD withdrew material critical of the Turkish president Recep Tayyip Erdoğan, a journalist from the magazine Der Spiegel compared this behaviour in an opinion article to the Politburo of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union.[16] To get rid of the "annoying image of state radio", the journalist recommends it would certainly be helpful to keep more distance from the government.[17]
Framing manual
[edit]Claudia Schwartz from the Neue Zürcher Zeitung reported in February 2019 the ARD wanted to impress upon its audience certain moral views. A manual from the "Berkeley International Framing Institute" (see sources below) was used internally in order to make ARD viewers consider their fees less as a compulsory contribution than as a kind of donation to a good cause.[18]
But the website Netzpolitik.org (who published the original document), came to the conclusion that "Many of the proposed frames, which are currently heating the minds of many critics, have never been used in public by the public broadcasters representatives. This also shows that the excitement about the report is too high."[19]
See also
[edit]- Television in Germany
- Zweites Deutsches Fernsehen (Second German TV channel)
- List of German-language television channels
Notes
[edit]- ^ German pronunciation: [ˌaːʔɛʁˈdeː] ⓘ; full name: Arbeitsgemeinschaft der öffentlich-rechtlichen Rundfunkanstalten der Bundesrepublik Deutschland, pronounced [ˈaʁbaɪtsɡəˌmaɪnʃaft deːɐ̯ ˌʔœfn̩tlɪçˈʁɛçtlɪçn̩ ˈʁʊntfʊŋkˌʔanʃtaltn̩ deːɐ̯ ˈbʊndəsʁepuˌbliːk ˈdɔʏtʃlant] ⓘ – "Working group of public broadcasters of the Federal Republic of Germany"; see § Name
References
[edit]- ^ "There for you. ARD" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-07-16.
- ^ "ARD Finanzbericht" (PDF). ARD. 2014. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2020-06-25. Retrieved 2017-01-11.
- ^ "ARD Mitarbeiter". ARD. 2015. Archived from the original on 2017-08-01. Retrieved 2017-01-11.
- ^ Anschlag, Dieter (2022-04-05). "2. ARD". www.mediadb.eu. Institut für Medien- und Kommunikationspolitik. Retrieved 2022-05-06.
- ^ "Startseite – Archivradio – Wissen – SWR2". swr.online. Retrieved 2018-03-14.
- ^ "Berichterstattung aus dem Ausland". ard.de. Retrieved 2021-11-18.
- ^ "Häufige Fragen / Das Korrespondenten-Netz". blog.tagesschau.de. Retrieved 2021-11-18.
- ^ "Berichterstattung aus dem Ausland". ard.de. Retrieved 2021-11-18.
- ^ "Auslandsstudios der ARD". ard.de. ARD. Retrieved 2018-03-14.
- ^ "Auslandsstudios – Organisation – Unternehmen". swr.de. Retrieved 2018-03-14.
- ^ WDR (2023-02-24). "WDR eröffnet ARD-Studio in Kiew - Presselounge - WDR" (in German). Retrieved 2023-02-24.
- ^ tagesschau.de. "Spanien und Portugal: Das ARD-Studio Madrid". tagesschau.de (in German). Retrieved 2023-11-08.
- ^ "Marion Schmickler". www1.wdr.de (in German). 2022-08-05. Retrieved 2023-11-08.
- ^ tagesschau.de. "Angola bis Südafrika: Das ARD-Studio Johannesburg". tagesschau.de (in German). Retrieved 2023-11-08.
- ^ "Studio Nairobi". www1.wdr.de (in German). 2017-09-25. Retrieved 2023-11-08.
- ^ Fleischhauer, Jan (2016-04-12). "ZDF ein Regierungssender: Kontrolliertes Fernsehen – Kolumne". Der Spiegel.
- ^ Fleischhauer, Jan (2019-02-14). "Manipulation: Schöner sprechen mit der ARD". Spiegel Online. Retrieved 2019-02-18.
- ^ Schwartz, Claudia. "Die ARD will mit Framing das Publikum einseifen". Neue Zürcher Zeitung (in German). Retrieved 2019-02-18.
- ^ Beckedahl, Markus (2019-02-17). "Wir veröffentlichen das Framing-Gutachten der ARD" (in German). Retrieved 2021-09-27.
Sources
[edit]- ARD: ARD Jahrbuch 2005 (in German). Hans-Bredow-Institut. 2005. ISBN 3-8329-1730-6. Archived from the original on 2006-09-02.
- Oxford International Study about the audience of Public Broadcasters (PDF). UK: Oxford University. 2019. p. 24. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2021-02-02.
- Criticism of ARD, ZDF (and others) during Corona (in German). die-tagespost.de. 2020.
- Criticism of Christine Strobl framed by NDR (in German). Daniel Bouhs, NDR. 2020.
- Framing Manual by ARD (PDF) (in German). Netzpolitik.org; ARD. 2019. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2021-07-18.
External links
[edit]- Official website (in German)
- Official information about ARD (PDF)
- Live ARD Radio. Archived 2019-11-28 at the Wayback Machine.
- ARD Radio Guide
- ARD on Instagram





